Learning Red Hat Linux doesn’t have to be complicated. Start with small steps and build your skills gradually.
Red Hat Linux is powerful and widely used in businesses and servers. Knowing it opens doors to many tech careers. But where do you begin? This guide breaks down learning Red Hat Linux into simple steps. You’ll understand the basics, explore commands, and eventually tackle advanced topics.
Each step builds on the last, making the journey manageable. Whether you’re a beginner or have some Linux experience, this structured approach helps you learn efficiently. Dive into this step-by-step guide and start your Linux journey today. You’ll find learning Red Hat Linux is easier than you thought.
Credit: www.redhat.com
Introduction To Red Hat Linux
Red Hat Linux is a powerful operating system that is widely used in the tech industry. It is known for its stability and reliability. Learning Red Hat Linux can open doors to many career opportunities. Whether you are a student or a professional, understanding this system is valuable. This introduction will guide you through its basics, helping you build a strong foundation.
What Is Red Hat Linux?
Red Hat Linux is a version of the Linux operating system. It is developed by Red Hat, a company known for its enterprise solutions. This system is open-source, meaning its code is freely available. It runs servers, desktops, and even cloud environments. Many businesses use Red Hat Linux for its security and efficiency. Its popularity in the industry makes it a crucial skill for tech enthusiasts.
Importance For Beginners
Starting with Red Hat Linux provides a solid base in the world of Linux. It teaches fundamental concepts that apply to other Linux distributions. Beginners can explore command line tools, system administration, and networking. Understanding these basics is essential for any IT professional. Red Hat Linux also offers certification programs. These programs validate your skills, boosting your job prospects. For those entering the tech field, learning Red Hat Linux is a wise choice.
Setting Up Your Environment
Embarking on the journey to master Red Hat Linux begins with setting up the right environment. This initial step is crucial as it lays the foundation for your learning experience. A well-prepared environment can make your path smoother and help you avoid common pitfalls. Let’s dive into how you can set up your environment effectively and ensure you’re ready to learn Red Hat Linux.
Choosing The Right Hardware
Your hardware is the backbone of your learning experience. You don’t need the latest or most expensive equipment, but you do need a machine that can handle the requirements of Red Hat Linux.
- Processor: Aim for at least a dual-core processor. This ensures that your system can manage multiple processes without slowing down.
- Memory: 4GB of RAM is a good starting point. If you can upgrade to 8GB or more, you’ll have a more seamless experience.
- Storage: A minimum of 20GB of free space is necessary. Consider using SSDs for faster boot times and better performance.
Think about your future needs. Will you be running complex applications or multiple virtual machines? Adjust your hardware choices accordingly.
Installing Red Hat Linux
Once your hardware is ready, the next step is installing Red Hat Linux. The installation process can seem daunting, but with the right approach, you can master it.
- Download the ISO: Visit the Red Hat website and download the latest ISO image. Make sure you choose the correct version for your system architecture.
- Create a Bootable USB: Use tools like Rufus or Etcher to create a bootable USB drive. This will be used to install the OS on your machine.
- Boot and Install: Restart your computer and boot from the USB. Follow the installation prompts carefully, selecting your preferences as needed.
Have you thought about dual-booting? If you’re not ready to commit fully, dual-booting allows you to explore Red Hat Linux while keeping your current OS intact.
As you proceed, remember that every challenge you face is an opportunity to learn. Setting up your environment correctly will empower you to tackle Red Hat Linux with confidence and enthusiasm.
Basic Linux Commands
Learning Red Hat Linux can be easy with basic Linux commands. Start with simple tasks like navigating directories and managing files. Progress gradually to more complex operations, such as using text editors and handling permissions.
Learning Red Hat Linux can be a rewarding journey, especially when you get a handle on the basic Linux commands. These commands are the backbone of navigating and managing your Linux environment effectively. Understanding them not only boosts your confidence but also enhances your productivity as you interact with the system. ###Navigating The File System
Navigating the Linux file system is like exploring a new city. You need to know the main streets and landmarks to find your way around. The `cd` command is your primary mode of transport, allowing you to change directories with ease. Want to know where you are? Use the `pwd` command to print your working directory. It’s like checking your current location on a map. Listing files in your current directory is simple with the `ls` command. This is your window to see what’s around you. Try adding options like `ls -l` for more details or `ls -a` to view hidden files. ###Managing Files And Directories
Managing files and directories is about organization and control. The `touch` command lets you create new files instantly. It’s as if you’re adding new items to your toolkit. Need a new folder? Use `mkdir` to make directories and `rmdir` to remove them when they’re no longer needed. It’s like organizing your workspace by adding and removing shelves. Copying files is simple with `cp`, and moving them can be done with `mv`. These commands are like rearranging your workspace efficiently. Remember, `rm` deletes files, but use it carefully—you don’t want to accidentally throw something important away. These basic commands open up a world of possibilities in Red Hat Linux. What will you create or organize today?Understanding The Red Hat Interface
Learning Red Hat Linux is an exciting journey. It opens doors to powerful tools. The interface of Red Hat Linux is key to this journey. Understanding it helps you navigate the system effectively. Red Hat offers two main interfaces: Graphical and Command Line. Each has its unique features and uses. Let’s explore them.
Graphical User Interface
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) is user-friendly. It provides visual elements like windows and icons. This interface is ideal for beginners. It resembles other familiar operating systems. You interact with it using a mouse and keyboard. The GUI includes applications for file management and system settings. This makes it easy to perform basic tasks. Adjusting system settings is simple with the GUI. You can also manage applications without complex commands. The GUI helps users to understand system structure visually.
Command Line Interface
The Command Line Interface (CLI) is powerful and efficient. It allows direct communication with the system. Users type commands in a terminal window. This interface offers greater control over the system. Experienced users prefer the CLI for complex tasks. It requires memorizing specific commands. The CLI is essential for managing servers and networks. It provides access to advanced features of Red Hat Linux. Mastering the CLI enhances productivity and efficiency. It is vital for automating tasks and scripting.
Package Management Basics
Learning Red Hat Linux is an exciting journey, and understanding package management is crucial. Package management is the backbone of maintaining and updating your system efficiently. It allows you to install, update, and remove software seamlessly. Whether you’re setting up a development environment or just tinkering with your system, mastering these basics will save you time and frustration.
Using Rpm
RPM stands for Red Hat Package Manager, and it’s a powerful tool for handling software packages. Imagine RPM as the gatekeeper for software installations. It ensures that packages are correctly installed and working harmoniously.
To install a package using RPM, you use the command rpm -i package-name.rpm. It’s straightforward, but what happens if something goes wrong? RPM provides feedback, helping you troubleshoot issues like dependency errors.
Updating a package is just as easy. Use rpm -U package-name.rpm. This replaces the old package with the new version. It’s like upgrading your smartphone’s OS—simple, yet effective.
What if a package causes trouble? You can remove it with rpm -e package-name. This keeps your system clean and ensures that only necessary software remains.
Working With Yum
YUM, which stands for Yellowdog Updater Modified, simplifies package management further. It’s like RPM’s cooler cousin, handling dependencies automatically. No more hunting down missing libraries!
To install a package with YUM, use yum install package-name. It checks for dependencies and installs them if needed. This makes your life easier, especially when you’re not sure what a package needs.
Updating all packages is a breeze with yum update. It’s like having a personal assistant that keeps everything current. This ensures your system is secure and runs smoothly.
Ever wondered about removing multiple packages at once? YUM lets you do that with yum remove package-name. It’s efficient and saves time, allowing you to focus on what truly matters.
Do you recall a time when installing software felt like piecing together a jigsaw puzzle? With RPM and YUM, package management becomes intuitive and organized. Are you ready to dive deeper into these tools and transform your Red Hat Linux experience?

Credit: developers.redhat.com
System Configuration And Management
Discovering Red Hat Linux starts with understanding the basics of the operating system. Follow step-by-step tutorials to configure and manage system settings effectively. Gradually progress to advanced tasks, ensuring a solid foundation in Linux system administration.
Learning Red Hat Linux can be a rewarding journey, especially when you master the art of system configuration and management. Understanding how to configure and manage your system will empower you to run a seamless and efficient environment. It’s like having the keys to your digital kingdom, enabling you to customize and control your system according to your needs.Network Settings
Getting your network settings right is crucial for connecting to the world. Start by learning how to configure your IP address. This can be done using the `nmtui` command in the terminal, which provides a simple text-based interface. Next, explore how to manage DNS settings. These settings ensure your system knows where to look when accessing websites. You can edit the `/etc/resolv.conf` file to add or update DNS servers. Lastly, practice setting up a static IP. This is useful for servers that need a consistent address. Simply edit the `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0` file to specify your desired IP address.User Account Management
Effective user account management is essential for system security and organization. Begin by creating a new user with the `useradd` command. For instance, `sudo useradd yourusername` will create a new user account. You should also learn to set and change passwords using the `passwd` command. Keeping passwords secure and updated is a fundamental security practice. Additionally, familiarize yourself with managing user permissions. Use the `usermod` command to add users to groups, granting them additional privileges. This allows you to control who can access and modify files on your system.Have you ever considered how these skills could make you a more efficient and secure Linux user? By diving into network settings and user management, you’re not just learning commands; you’re enhancing your system’s reliability and security. Take each step at your own pace, and soon, you’ll master system configuration and management in Red Hat Linux.
Security Practices
Learning Red Hat Linux involves mastering its security features. Security practices protect your system from threats. They ensure your data remains safe. Two crucial areas are firewall configuration and SELinux policies. Each plays a vital role in system security.
Firewall Configuration
Firewalls control the flow of data in and out of your network. They act as a barrier against unauthorized access. Red Hat Linux uses firewalld for managing firewall rules. Start by understanding the basic commands. Learn how to enable, disable, and check the status. Familiarize yourself with creating and managing zones. Zones define the trust level of network connections. Practice adding and removing services from zones. This ensures only trusted services communicate.
Selinux Policies
SELinux adds another layer of security. It enforces strict access controls based on policies. These policies define what processes can access. They also dictate how they interact with files and directories. Start by learning the SELinux modes. There are enforcing, permissive, and disabled modes. Enforcing mode applies the policies strictly. Permissive mode logs actions without enforcing them. Understand how to switch between these modes. Explore tools like setenforce and getenforce for this task.
Learn to use semanage and chcon commands. These help modify SELinux policies and context. Always check logs for SELinux-related issues. The audit.log file provides detailed information. Review it regularly to catch potential problems early.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Learning Red Hat Linux can be challenging, but troubleshooting common issues simplifies the process. Start with basic command-line skills. Gradually explore system administration tasks to build confidence.
Learning Red Hat Linux can be challenging. Troubleshooting skills are crucial. They help you resolve issues quickly. Problems may arise during your learning journey. Understanding common issues helps you learn better. Here is a guide on how to troubleshoot effectively.System Diagnostics
System diagnostics are important in problem-solving. They help identify the root cause. Use tools like `top` and `htop`. They show system processes and resource usage. Understand the outputs of these commands. This helps pinpoint the issue. The `dmesg` command displays kernel-related messages. It shows hardware errors or driver problems. Check the system logs using `journalctl`. They provide detailed error information. Keep your system updated. Updates often fix known issues.Fixing Boot Problems
Boot problems can be frustrating. But they are usually fixable. Start with checking the GRUB configuration. Incorrect settings can stop your system from booting. Use a live CD or USB to access your system. This allows you to edit GRUB settings. Check if essential files are missing. Missing files can lead to boot failures. Use `fsck` to check and repair the file system. This tool fixes corrupted files. Always back up your data before running `fsck`. Ensure your bootloader points to the correct kernel. Wrong kernels can cause boot loops. Update your initramfs with `dracut`. This ensures all necessary drivers are loaded. By following these steps, you can solve common issues efficiently. This builds confidence in handling Red Hat Linux challenges.Resources For Further Learning
Explore step-by-step guides and online tutorials for learning Red Hat Linux effectively. Check forums and communities for shared knowledge and real-life experiences. Free courses and video lessons offer practical insights into mastering Linux commands.
Learning Red Hat Linux can feel daunting. The right resources make all the difference. Quality materials deepen understanding and build confidence. Whether online courses, forums, or tutorials, varied resources enhance learning.Online Courses And Tutorials
Explore online courses for structured learning. Websites like Udemy and Coursera offer comprehensive lessons. They cover basics to advanced topics. Video tutorials on YouTube help with visual understanding. Many are free and cater to beginners. These resources allow learning at your pace. Interactive platforms like Codecademy provide hands-on practice. They reinforce concepts with real-world scenarios.Community Support And Forums
Join forums to connect with other learners. Communities like Reddit and Stack Exchange offer valuable insights. Members share tips, solve problems, and provide encouragement. Active participation in forums boosts your learning. Engage with experts and novices alike. This interaction builds a deeper understanding. Online communities often host events and webinars. These opportunities expand your knowledge and network.
Credit: www.amazon.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Red Hat Training Free?
Red Hat training is not free. They offer various paid courses and certifications. Some free resources may be available, but comprehensive training typically requires a fee. Explore their official website for detailed pricing and course offerings.
What Programming Language Does Red Hat Use?
Red Hat primarily uses programming languages like C, C++, Python, and Java. These languages are integral to its software development. Python is commonly used for scripting and automation tasks, while Java is preferred for enterprise applications. C and C++ are foundational for system-level programming in Red Hat products.
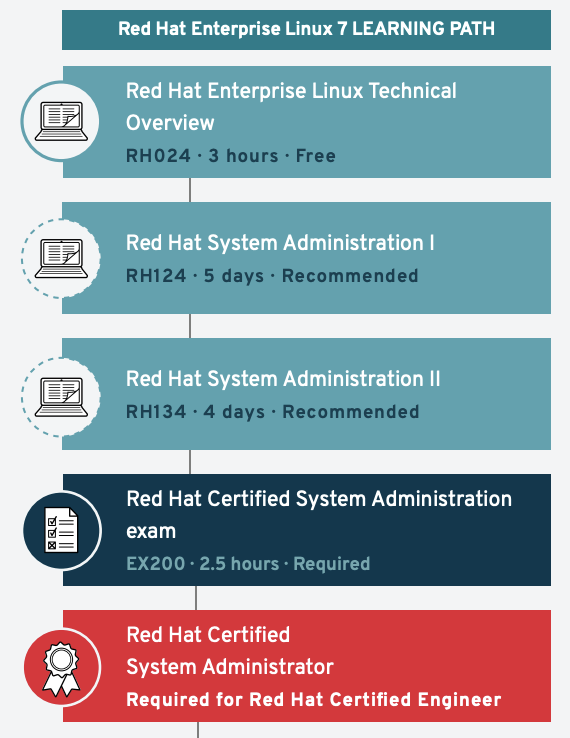
How To Get Red Hat Linux Certification?
To get Red Hat Linux certification, enroll in a Red Hat training course. Prepare using official study materials and practice exams. Schedule and pass the relevant certification exam at a testing center. Certifications include RHCSA, RHCE, and RHCA, offering different levels of expertise.
How To Start Linux Step By Step?
Install a Linux distribution like Ubuntu or Fedora from their official website. Create a bootable USB using tools like Rufus. Restart your computer and boot from the USB. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. Configure your settings and start exploring Linux.
Conclusion
Learning Red Hat Linux step by step is achievable. Start with basic commands. Practice regularly to build your skills. Use online tutorials and forums for guidance. Connect with others who share your interest. Hands-on experience is crucial for understanding. Stay patient and persistent in your learning journey.
Each lesson learned brings you closer to proficiency. Red Hat Linux skills open doors in tech careers. Keep exploring and growing your knowledge. Your effort will pay off in the end. Happy learning!
